The Air Handler is an important component of an air conditioning system that is responsible for processing air and distributing it to various areas within a building.
Working Principle:
Air Handler works similarly to the core of a central air conditioning system, and its main tasks include:
1. Air intake: The fan is activated to draw outside or indoor air into the Air Handler Unit.
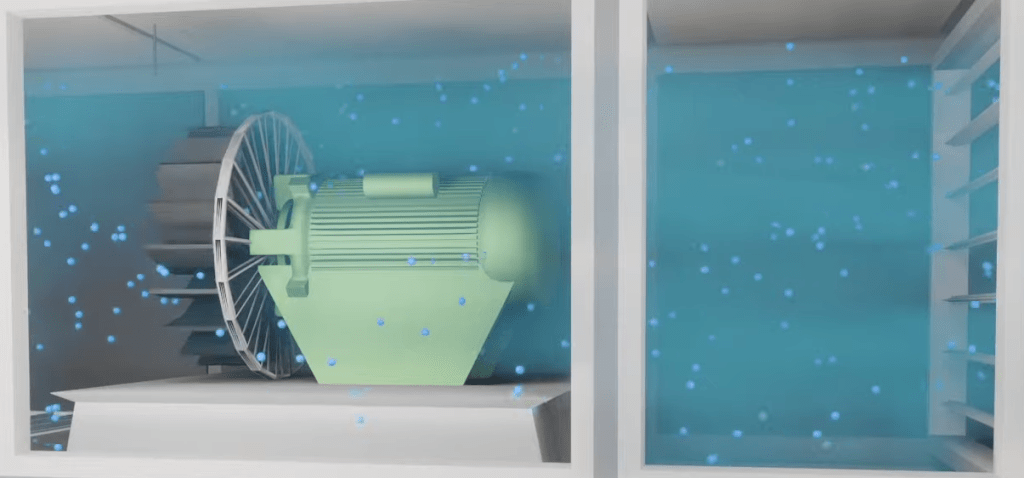
2. Mixing section: If heating or cooling is required, the air passes through the appropriate coils. For example, in winter, the air absorbs heat through the heating coils; in summer, the air releases heat through the cooling coils.
3. Humidity Adjustment: As needed, air passes through humidifiers or dehumidifiers to adjust humidity.
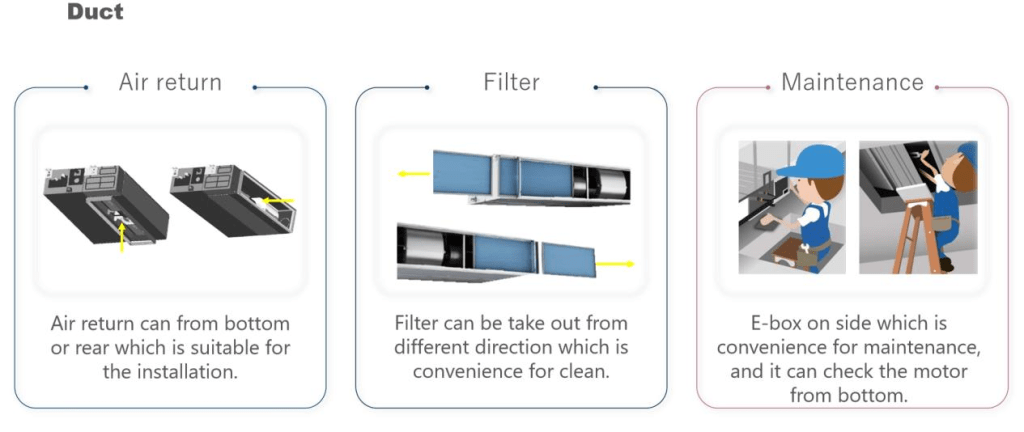
4. Filtration section: the air passes through a filter to remove dust and other particles and improve air quality.
5. Air supply: Treated air is sent into the indoor space through the duct system to meet the needs of the indoor environment.

6.Circulation: Indoor air may be re-drawn into the air handling unit or some of the new air may be mixed with return air to achieve a balance between energy efficiency and air quality.
Air Handler is usually made up of the following main components:
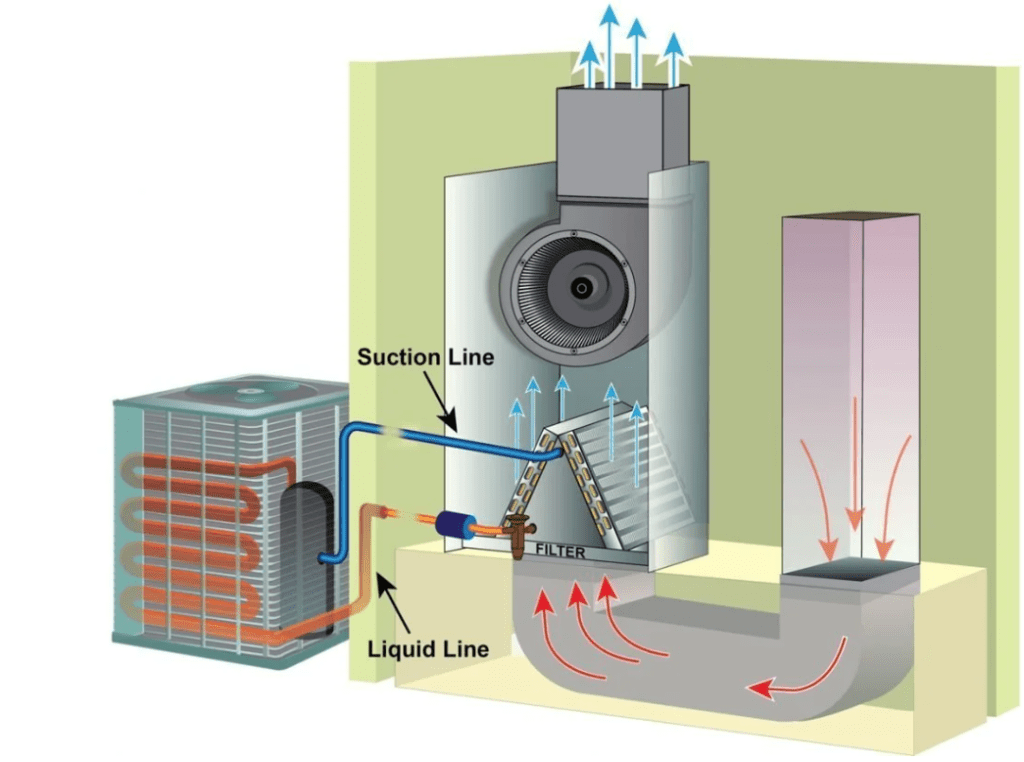
- Evaporator Coil:
The evaporator coil inside the air handler cools air by absorbing heat as warm air passes over it, facilitated by refrigerant that evaporates at low temperatures. - Blower Motor:
The blower motor moves air through the air handler and ducts, cooling it over the evaporator coil before distribution to rooms, crucial for system efficiency. - Air Filter:
The air filter traps airborne particles to improve indoor air quality and protect the HVAC system, essential for system longevity and occupant comfort. - Electrical and Electronic Parts:
These components control the blower motor and system operation, ensuring proper start-up, runtime, and shutdown, while adjusting settings for temperature and humidity control.

Comparison to Split Air Conditioners:
Air Handler is functionally and structurally similar to the indoor unit in a split air conditioning system (often referred to as an indoor unit), but they are typically integrated into a centralized HVAC system (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning system) rather than a standalone split air conditioning system. Here are the differences and potential advantages of an Air Handler versus a split AC indoor unit:
- System Integration:
· Air Handler: typically used as part of a central HVAC system in conjunction with a heat pump, natural gas furnace or other heating unit, and a whole-home ventilation system. It provides year-round cooling and heating and distributes air to multiple rooms through a network of ducts.
· Split AC: usually used for cooling only, sometimes with heating capability, but usually serving only one or a few adjacent rooms. - Installation and design:
· Air Handler: designed to be concealed in an attic, basement, or dedicated air conditioning room and connected to the living space by air ducts and vents. It is usually larger to accommodate the air needs of the entire home.
· Split AC: Usually smaller, it can be mounted directly on the wall or ceiling, with an exterior design that focuses more on blending in with the interior decorating. - Function and performance:
· Air Handler: As part of a centralized system, it can provide more even air distribution and better temperature control. It can also be integrated with various air purification and humidity control functions.
· Split AC: usually focuses more on quick cooling or heating of localized areas and may not have the advanced features of air filtration or humidity control. - Maintenance & Servicing:
· Air Handler: Specialized maintenance, covers entire system.
· Split AC: Simple maintenance, focuses on unit cleaning/filter replacement. - Energy efficiency and cost:
· Air Handler: may be more efficient as a centralized system because it can be designed to serve the overall needs of the entire home. Proper sizing and configuration can reduce energy waste.
· Split AC: usually designed for a specific area and may be more energy efficient because it serves only one room or area.
Overall, the Air Handler has an advantage in providing overall indoor comfort and air quality, while a split AC indoor unit may be more flexible and efficient for rapid cooling and heating of specific zones. Which system to choose depends on the size, design, budget and personal preference of the building.
Why Americans prefer Air Handler over split AC:
In the United States, central HVAC systems, including Air Handlers, are prevalent, while split air conditioning systems are more common in certain regions of Asia and Europe. Reasons for the popularity of Air Handlers in the U.S. may include:
1.Building Standards: Many U.S. structures are designed for centralized HVAC systems, incorporating an air handler and duct network for efficient air distribution.

2.Climate Comfort: Extreme weather conditions in some U.S. regions necessitate consistent indoor temperatures, achievable through centralized HVAC systems.
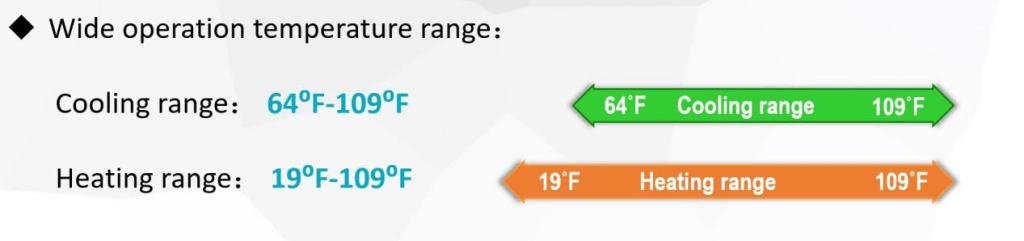
- Energy Efficiency: Central HVAC systems can be optimized for overall home efficiency, reducing energy waste, particularly in larger residences.
- 4.Air Quality: Advanced filtration in centralized systems improves indoor air quality, crucial for allergy sufferers.
- 5.Maintenance Ease: While centralized systems may require specialized maintenance, they offer simplified control and management compared to multiple split units.
6.Noise Reduction: Outdoor placement of noise sources in centralized systems minimizes indoor noise levels for a quieter living environment.

- Aesthetic Appeal: Centralized systems maintain interior design integrity by eliminating the need for multiple indoor units.
However, split air conditioners are also utilized in the U.S., particularly in smaller or older buildings lacking central HVAC infrastructure.
The importance of having a professional HVAC team properly install your HVAC unit includes:
1.Proper Design and Sizing: Professionals ensure the system is designed and sized correctly for the building, optimizing performance and longevity.

- High-Quality Installation: Skilled installers follow manufacturer and industry standards for a safe, efficient, and properly functioning system.
- Safety: Professional installation minimizes risks such as leaks or electrical issues, ensuring a safe operating environment.
- Energy Efficiency: Experts optimize system sealing and setup to reduce energy waste and costs.
- Commissioning and Calibration: Professional dealers fine-tune new systems for peak performance and component harmony.
- Warranty and Service: Installers often provide post-installation support, including warranties and maintenance services.
- Compliance: Professionals navigate local codes and regulations, ensuring the installation meets all legal and industry standards.
- Comfort: Proper installation guarantees even air distribution and consistent indoor temperatures for enhanced comfort.
In essence, a licensed HVAC dealer’s correct installation is key to a system’s performance, safety, energy efficiency, and long-term savings, as well as ensuring a comfortable living or working environment.
Choose ZERO’s professional HVAC team for expert design, high-quality installation, and guaranteed comfort, ensuring optimal system performance, safety, and energy efficiency for your heating and cooling needs.